Implementing CORS in API Gateway
Browsers are really smart. They do their best to ensure that they keep the users safe. One of the ways that they do this is by making sure you don't make API requests to other domains. This is called the same-origin policy. It is a security measure that prevents malicious scripts from accessing data from other domains. However, this is also a pain when you want to set up an API somewhere like API gateway and access it from your browser. This is where CORS comes in.
What is CORS?
CORS stands for Cross-Origin Resource Sharing. It is a protocol that enables scripts running in the browser to interact with resources from a different domain. In plain English, if you're writing a React App that needs to make calls to an API backend running on a different domain, you'll need CORS.
CORS has a couple of different request types. A common one is a simple request, but this is only available for GET, HEAD, and POST requests, and even then only for certain content types (not JSON). So for the purposes of building an API, we'll need to use a preflight request. This is a request that the browser sends to the server to ask if it's okay to make the request. You may have seen this in your network tab before. It's an OPTIONS request that has a bunch of headers on it.
Which headers can I set for a preflight request?
There are a few headers that you can set on a preflight request. The most common ones are:
Access-Control-Allow-Origin: This header tells the browser which domains are allowed to access your API. If you set this to*, then any domain can access your API. If you set it to a specific domain, then only that domain can access your API. You can also set it to a list of domains.Access-Control-Allow-Methods: This header tells the browser which HTTP methods are allowed for your API. This is a comma separated list of methods allowed, e.g. GET, PUT, POST, DELETE. It can also be set to*which will allow all methods.Access-Control-Allow-Headers: This header tells the browser which headers are allowed for your API. Here you can set a comma separated list of headers that are allowed. For our case we'll need to setContent-Type. It can also be set to*which will allow all headers.Access-Control-Allow-Credentials: This header tells the browser whether or not it should send cookies with the request. This header is optional, but if you want to use cookies with your API, then you'll need to set it.Access-Control-Max-Age: This header tells the browser how long it should cache the preflight response for. This header is optional, but if you want to use cookies with your API, then you'll need to set it. Even though this is optional, it's a good idea to set it to a reasonable value, I usually set it to 10 minutes. This will prevent the browser from sending a preflight request every time you make a request to your API and should improve performance.
How do I enable CORS in API Gateway?
Looking at the API Gateway console, you'll see that I've already set up a route which I want to set up CORS for. Assuming AWS doesn't change it again, you'll see in the left hand pane under Develop, a section called CORS. Click on that and you'll see a bunch of options.
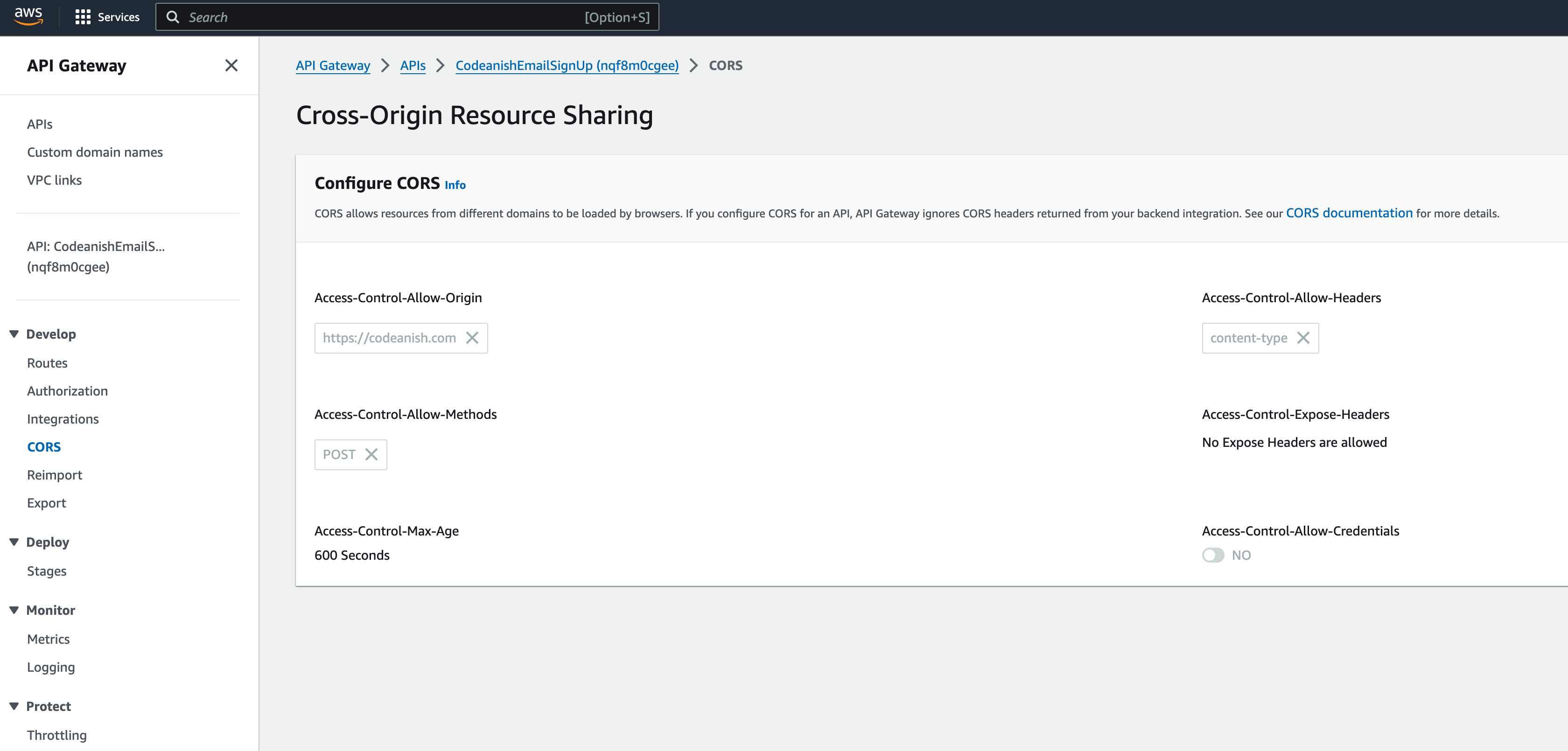
The CORS section of the API Gateway console provides you with the ability to set your various
CORS headers. I want to lock down my particular API to only allow requests from my domain, so
I'll set the Access-Control-Allow-Origin header to https://codeanish.com. For this API, I am
only using it for email list signups so I only need to allow POST requests, so I'll set the
Access-Control-Allow-Methods header to POST. I also need to allow the Content-Type header
so I'll set the Access-Control-Allow-Headers header to Content-Type. I'm not using cookies
for this API so I'll leave the Access-Control-Allow-Credentials header set to NO. Finally, I'll set
the Access-Control-Max-Age header to 600 seconds.
Once you've set all of your headers, click the Deploy button at the top of the page. This will deploy your API with the new CORS settings. You should now be able to make requests to your API from your browser.
I can't tell you how many times I've been developing an API and I've forgotten to set up CORS. Hopefully you can see that it's not super complicated to set up on API Gateway. If you happen to be hosting your API using something else e.g. Express/FastAPI/Flask, then you'll need to set up CORS there.